- Jay Schiff
- 0 Comments
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a form of non-invasive treatment that is growing in popularity for its applicability across several mental health categories. Today, it is receiving increasing awareness because of its potential as a treatment for bipolar disorder.
The FDA is responsible for regulating medical devices. Before medical devices can be legally sold or used in the United States to treat certain conditions, evidence has to be presented that they are safe and effective for that particular use. Only with FDA-approved TMS can many health insurance providers, for example, offer coverage for its use for mental health treatments.
Receiving approval by the FDA confirms that a given medical device has gone through rigorous testing and offers a viable form of treatment for different conditions. With TMS FDA-approved, individuals who are struggling with things like OCD or treatment-resistant depression now have access to a new form of care to manage their symptoms.
Is TMS FDA-approved for bipolar?
TMS bipolar depression FDA status was designated in 2020 as “breakthrough device designation” specifically for bipolar disorder. This TMS bipolar FDA means the FDA has approved the device to be medically safe for consumers and to be marketed and sold throughout the United States.
What is the Breakthrough Devices designation?
This program is a voluntary program for specific medical devices and combination products that could offer more effective treatment for many conditions. The program is overseen by the FDA, but it’s intended to provide healthcare providers and patients with timely access to medical devices that conform to device safety and effectiveness standards.
The program provides manufacturers with an opportunity to directly interact with the FDA, receive feedback on medical devices, and expedite the review and approval of eligible devices for use in treating several conditions.
Why the FDA TMS designation matters
The FDA TMS approval for breakthrough devices means manufacturers of TMS medical devices can focus on a data development plan and a clinical protocol agreement moving forward, which can expedite the review of the device beyond just market authorization. At this time, the designation means that the FDA has approved the device for market authorization, but the specific use as a treatment for bipolar is pending final approval.
The next steps for TMS FDA approval for bipolar disorder are the same as the steps that were followed for FDA TMS approval for depression or OCD: evidence through scientific research and clinical trials must be presented to the FDA to initiate a formal review, after which the FDA can formally approve the device for bipolar disorder.
Current studies: Benefits of TMS for bipolar
So, what studies currently exist? For the last two decades, several studies have examined the efficacy of TMS for bipolar treatment.

2021
Work in 2021 conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of the efficacy of TMS treatment for bipolar depression. It specified stimulation of the prefrontal cortex, confirming that those who underwent active repetitive TMS sessions had a nearly three times higher response rate to improved bipolar depression symptoms compared to those taking other medications and treatments.
Another study from the same year reviewed 31 clinical trials and research papers confirming that participants with bipolar depressive episodes had better results in terms of mood stabilization and doing away with suicidal behavior after receiving transcranial magnetic stimulation, although findings, as it pertains to manic episodes, remain mixed.
2019
In 2019, one study noted that many people struggling with bipolar disorder do not benefit from traditional pharmacotherapy, and for those, TMS offers a non-invasive neuromodulation technique that could target the hyperactive or hypoactive cortical areas of the brain.
Results indicated potential for the efficacy of repetitive TMS in reducing the depressive symptoms of bipolar disorder, with mixed findings for the efficacy of TMS when it comes to mania.
2018
Work in 2018 reviewed the safety data from a controlled trial of TMS treatment in bipolar disorder. Under normal circumstances, bipolar depression presents with cognitive deficits that don’t resolve following pharmacological treatment. Deep TMS was able to target areas responsible for controlling working memory, language, and attention, after which there was statistically significant cognitive Improvement, particularly for the language areas of the brain following several weeks of TMS treatment.
2017
In 2017, a double-blind, randomized clinical trial reviewed the efficacy of deep TMS for bipolar depression. Patients received 20 sessions targeting the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. The primary outcome showed a significant change in the Hamilton depression rating scale from the start through the end of the four weeks. Secondarily, there were changes in depressive symptoms two months later with positive remission.
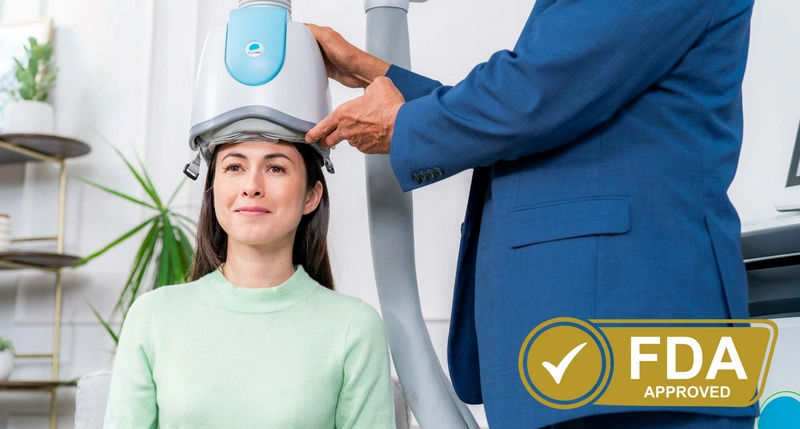

2004
In 2004, studies focused on manic episodes as they relate to transcranial magnetic stimulation and found that after four weeks of TMS treatment, there was a sustained reduction in manic symptoms across all patients, confirming that targeting the right prefrontal cortex offers rapid and safe relief for bipolar mania.
2003
A 2003 pilot study initiated the safety and efficacy of TMS for bipolar affective disorder. During these clinical trials, the left prefrontal cortex was stimulated on a daily basis for several weeks. Results confirmed that stimulation to the targeted neural areas had no adverse effects, nor did it induce mania in those who are struggling with depressive episodes.
Overall, the benefits of receiving the breakthrough device designation for medical device companies mean that the FDA has approved the use of TMS as safe and effective. While official approval has been granted for the treatment of depression and OCD, there are pending potential benefits of TMS as an FDA-approved treatment option for bipolar disorder.
Even now, the FDA-approved TMS can change clinical practices and patient outcomes. Patients can work with TMS treatment centers to get help that might not come from medication. Healthcare providers can refer patients for alternative TMS treatment, particularly when pharmacological interventions are unsuccessful. Overall, the broader mental health community is now positioned to benefit from newer, safer, non-invasive treatment options without harmful side effects.
Summing Up
The FDA’s Breakthrough Device Designation for TMS in bipolar disorder has several implications, not least of which is that with increased interest in the use of TMS for bipolar treatment, the FDA will move into a formal review process whereby they review the existing literature and consider formal approval. Patients, healthcare providers, and researchers should continue to learn more about TMS and its potential in bipolar disorder treatment.