Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) and Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) are both neuromodulation techniques used in the treatment of neurological and psychiatric disorders. Both conditions have many similarities but they are two separate therapies and there are key differences to understand when considering the two.
Today, there is an increasing interest in these therapies, and there is a need for comparative analysis to guide treatment decisions. It is important to understand the mechanisms and applications of both DBS and TMS as therapeutic interventions for neurological and psychiatric disorders.
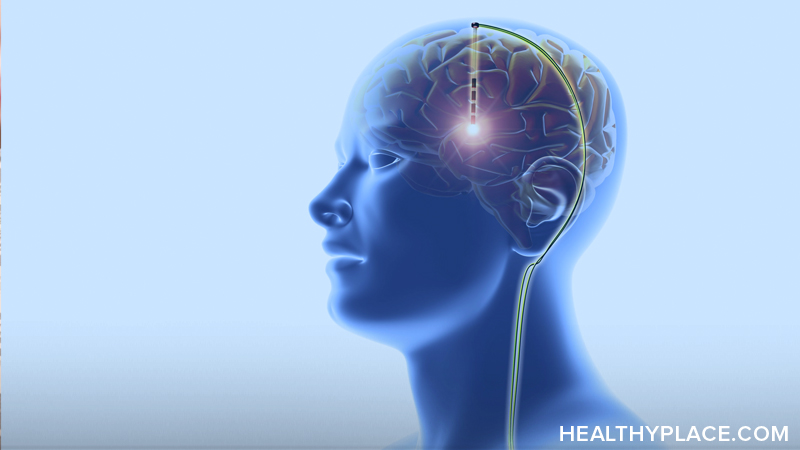
Mechanisms and Applications of DBS
Deep brain stimulation is a more invasive medical procedure that actually implants electrodes into your brain. The procedure makes small holes in your skull through which electrodes are placed in your brain after which electrical pulse generators are implanted somewhere around your collarbone or chest. Wires are moved in your body to connect the two so that you can send electrical impulses to your brain.
This then is controlled by doctors and devices to manage electrical impulses that are sent to different areas of your brain and control things that are not firing the way they should.
Mechanisms and Applications of TMS
With TMS deep brain stimulation options, there are several regions of the brain that can be targeted in order to address varying mental health conditions, including the following:
- the medial prefrontal cortex,
- dorsolateral prefrontal cortex,
- inferior frontal gyrus,
- superior parietal lobe,
- middle temporal gyrus,
- superior temporal sulcus,
- lateral occipital cortex
- supplementary motor area/paracentral gyrus.
With transcranial magnetic stimulation it’s not uncommon for multiple areas to be targeted in order to address symptoms of a single condition. in anxiety disorders, the lateral prefrontal cortex may not be performing the way it should in which case hypoactivity will be addressed but at the same time the amygdala or medial prefrontal cortex might be overactive in which case the hypersensitivity will be addressed.
Throughout the brain, the mechanisms of action for TMS work by sending magnetic pulses to regions that may be under or overperforming, encouraging neural connections or blood vessels to fire the way they should, increasing blood flow to otherwise dormant areas, and utilizing the neuroplasticity of the brain to reach deeper areas that medication might not be able to reach and to encourage neurotransmitter systems and synapses to work the way they should.
Efficacy and Clinical Outcomes of DBS
The FDA has approved deep brain stimulation for treating certain conditions, primarily epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, and obsessive-compulsive disorder. Deep brain stimulation is an effective treatment for serious conditions, but it is intended as a long-term treatment because it does require minor surgery and is a somewhat permanent solution.
With deep brain stimulation it can take several months before your doctor is able to customize the electrical stimulation settings based on your needs. This can be a lengthy process of trial and error that brings with it additional risks and discomfort.
However, it can provide lasting relief from symptoms of major neurological disorders.
Efficacy and Clinical Outcomes of TMS
Hundreds of studies have reviewed the efficacy and clinical outcomes of deep brain TMS as well as alternative therapies, particularly for mental health conditions like anxiety, OCD, and depression.
- Literature reviews for MS confirm that TMS offers short-term promise, optimizing functional brain activity.
- Other evidence suggests that TMS is effective in helping with movement-dependent stroke recovery
- Several studies found that TMS is useful in the treatment of anxiety disorders.
- Literature reviews have concluded that it works well for depression, offering significant relief for over fifty percent of patients immediately, with one-third going into remission entirely.
- TMS for OCD offers relief from symptoms within two weeks of treatment.
- Researchers concluded that TMS can decrease pain severity for those with chronic pain like fibromyalgia.
- Research also supports the idea that TMS can be useful in relieving chronic migraines.
- Meta-analyses have concluded that TMS works well in treating substance abuse disorders and is something that can be used regularly to prevent relapse.
Safety and Adverse Effects of DBS
Deep brain stimulation is an invasive medical procedure, which means you have to undergo surgery. Undergoing surgery brings with it the risk of complications as well as recovery time. It can take six weeks before you’re allowed to do strenuous activity, and once your device is activated, you might need to keep the implant for several years.
Given that there are direct changes to your brain, this can also risk complications like cognitive issues, mood changes, or problems because of the hardware.
Safety and Adverse Effects of TMS
When you are comparing deep brain stimulation vs. TMS for safety and adverse effects, One of the biggest things that comes to the forefront of all studies is that transcranial magnetic stimulation has no real side effects. There is limited risk and next to no adverse effects associated with the procedure. Given that it is a non-invasive procedure that doesn’t rely on things like anesthesia, it’s also something that can easily be fit into any routine.
Cost Considerations and Accessibility of DBS and TMS
When looking at the cost considerations for deep brain stimulation TMS, there is usually a minimum requirement for how many sessions you need, and not all insurance companies will cover the cost.
It’s also important that you go to a qualified clinic to receive your TMS treatment and not all clinics are the same so you’ll have to be aware of what the accessibility is in your area.
Deep brain stimulation is much more expensive than transcranial magnetic stimulation because you have to pay for the surgery and the device. You’ll also have to pay for regular maintenance and surgery long-term, which can cost hundreds of thousands of dollars compared to the thousands of dollars that you pay for TMS.
Considerations for Treatment Selection
When you are deciding which option is best, you need to consider what you are trying to treat. If you are struggling with a neurological condition that needs to be altered with electrical stimulation on a regular basis, deep brain stimulation is a highly costly though effective option. For most people however, and for most mental health conditions, transcranial magnetic stimulation is a safer, effective, and more accessible option.
Summing Up
There are several alternative treatments today to help with mental health conditions and neurological conditions. Deep brain TMS options might be something to consider. It’s important that you navigate your decision-making process between deep brain stimulation vs. TMS based on accessibility, cost, safety, efficacy, and the mechanisms that are used.